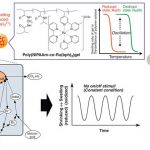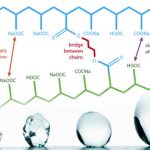
Copolymer chemistry
Copolymer, any of a diverse class of substances of high molecular weight prepared by chemical combination, usually into long chains, of molecules of two or more simple compounds (the monomers forming the polymer). The structural units derived from the different monomers may be present in regular alternation or in random order, or strings of several units of one kind may alternate with strings of another.
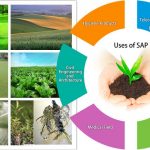
Superabsorbent polymers are now commonly made from the polymerization of acrylic acid blended with sodium hydroxide in the presence of an initiator to form a poly-acrylic acid sodium salt (sometimes referred to as sodium polyacrylate). This polymer is the most common type of SAP made in the world today. According to U.S Food & Drug Administration, sodium polyacrylate is listed in Food Additive Status List, but there are strict limitations.
Other materials are also used to make a superabsorbent polymer, such as polyacrylamide copolymer, ethylene maleic anhydride copolymer, cross-linked carboxymethylcellulose, polyvinyl alcohol copolymers, cross-linked polyethylene oxide, and starch grafted copolymer of polyacrylonitrile to name a few. The latter is one of the oldest SAP forms created.
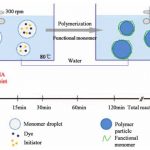
Today superabsorbent polymers are made using one of three primary methods: gel polymerization, suspension polymerization or solution polymerization. Each of the processes have their respective advantages but all yield a consistent quality of product.