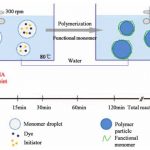
Gel polymerization
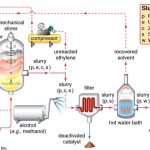
A mixture of acrylic acid, water, cross-linking agents and UV initiator chemicals are blended and placed either on a moving belt or in large tubs. The liquid mixture then goes into a “reactor” which is a long chamber with a series of strong UV lights. The UV radiation drives the polymerization and cross-linking reactions. The resulting “logs” are sticky gels containing 60-70% water. The logs are shredded or ground and placed in various sorts of driers. Additional cross-linking agent may be sprayed on the particles’ surface; this “surface cross-linking” increases the product’s ability to swell under pressure—a property measured as Absorbency Under Load (AUL) or Absorbency Against Pressure (AAP). The dried polymer particles are then screened for proper particle size distribution and packaging. The gel polymerization (GP) method is currently the most popular method for making the sodium polyacrylate superabsorbent polymers now used in baby diapers and other disposable hygienic articles.
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) is a technique widely used in biochemistry, forensic chemistry, genetics, molecular biology and biotechnology to separate biological macromolecules, usually proteins or nucleic acids, according to their electrophoretic mobility. Electrophoretic mobility is a function of the length, conformation and charge of the molecule. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis is a powerful tool used to analyze RNA samples. When polyacrylamide gel is denatured after electrophoresis, it provides information on the sample composition of the RNA species.
An inorganic sol–gel polymerization
An inorganic sol–gel polymerization process was used as a cross-linking reaction during three-dimensional (3D) bioprinting of cell-containing hydrogel scaffolds. Hybrid hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (HPMC), with a controlled ratio of silylation, was prepared and isolated as a 3D-network precursor. When dissolved in a biological buffer containing human mesenchymal stem cells, it yields a bioink that can be printed during polymerization by extrusion. It is worth noting that the sol–gel process proceeded at pH 7.4 using biocompatible mode of catalysis (NaF and glycine). The printing window was determined by rheology and viscosity measurements. The physicochemical properties of hydrogels were studied. Covalent functionalization of the network can be easily performed by adding a triethoxysilyl-containing molecule; a fluorescent hybrid molecule was used as a proof of concept.